MPEG-4 vs AVC/H.264 vs MP4. What is the difference?
MPEG-4 video, AVC/H.264, MP4 are all parts of the MPEG-4 group of standards which explains the confusion between them.
- MPEG-4 Part 2 Visual (ISO/IEC 14496-2) is a video coding standard released in 1999 as MPEG-4 video codec;
- MPEG-4 Part 10 Advanced Video Coding (ISO/IEC 14496-10) is a video coding standard released in 2003 as AVC/H.264 video codec;
- MPEG-4 Part 14 (ISO/IEC 14496-14): MP4 file format is a media container. It determines a method of storage rather than a compression algorithm.
AVC/H.264 codec took the best from MPEG-4 Visual, but these video formats are not backward compatible! MPEG-4 codec was pushed out of the market because AVC/H.264 provided a higher compression ratio. AVC/H.264 is the most popular format worldwide to this date. Video codecs are algorithms for encoding and decoding video data. Encoder compresses video streams, which reduces the amount of data for storage and transmission. Decoder reverses conversion for playout or editing a video stream. Container is a data storage. It can include video and audio sequences, subtitles, service information and metadata. The main difference is that a codec (video format) is an algorithm for encoding/decoding video data, and a container (file format) is a package in which a compressed video sequence is stored.
Examples of video codecs and media containers:
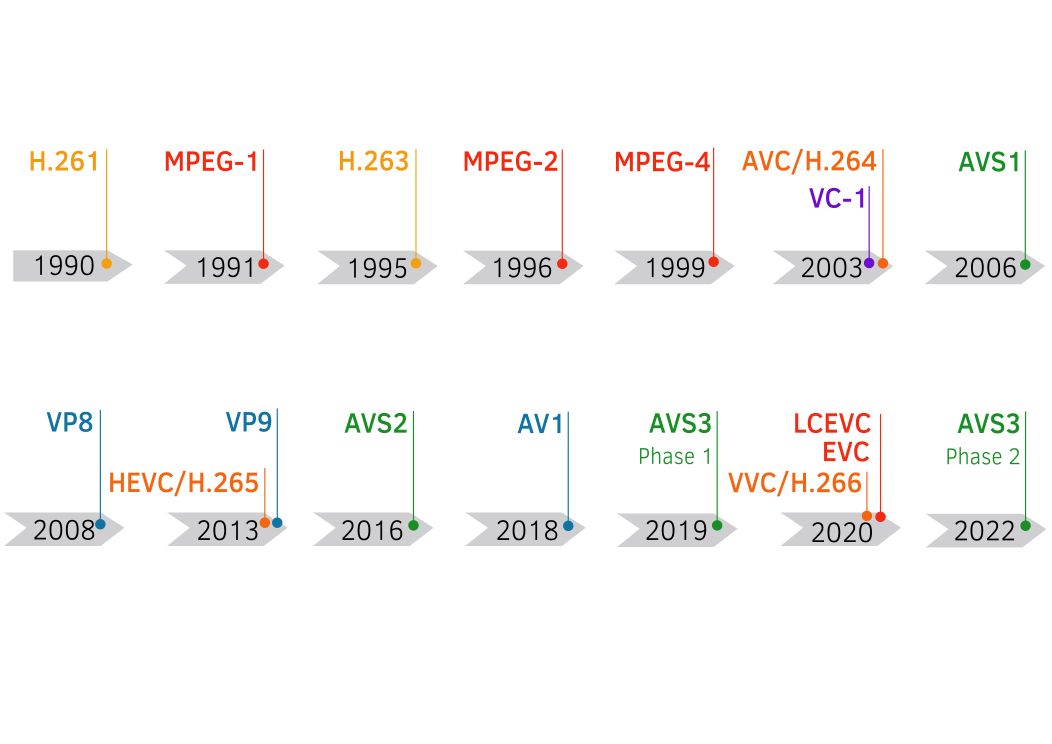
History of video codecs developments: